Prematurity: Assuring Good Start For Children Born Before 37 Weeks
- Par Kimeng Hilton
- 15 Nov 2025 09:08
- 0 Likes
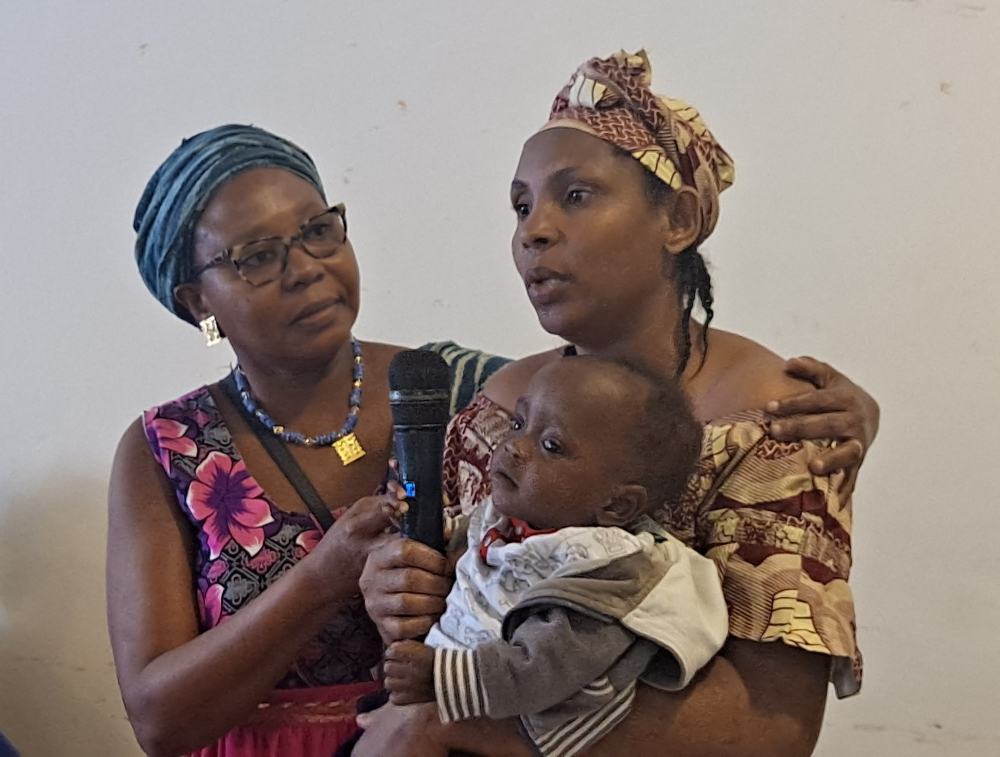

The Ministry of Public Health and partners on November 14, 2025 in Yaounde held a briefing for the media to mark World Prematurity Month.
As part of the Month of Prematurity running from November 1-30, 2025, Cameroon will on November 17, celebrate the 13th World Prematurity Day on the theme, “Giving premature babies a good start for a better future.” Taking advantage of the special month, the Ministry of Public Health, the United Nations Children’s Fund, UNICEF and other stakeholders on November 14, 2025 in Yaounde, organized an awareness session with the media on prematurity. Or premature children born before 37 weeks of gestation.
What Is Prematurity?
According to the World Health Organization, WHO, a premature newborn is a baby born before the completion of the full term of pregnancy - that is, before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Premature infants have immature organs which, depending on the gestational age, may not yet be capable of functioning adequately outside the uterus. As a result, preterm babies are at a significantly higher risk of death. Prematurity accounts for more than half of all neonatal deaths.
Worldwide Impact
“Every year, nearly 15 million premature births are recorded across the world. In Cameroon and elsewhere, one out of ten children is born premature. About 40-50 per cent of deaths amongst these babies are attributable to prematurity. Nevertheless, government and partners have been making efforts to take charge of these babies in their communities, at the central level through the coordination of field activities, and finally by ensuring good governance in the healthcare system through good policies and strategies,” said Dr. Ebongo Zacchaeus Nanje, the Director of Family Health in the Ministry of Public Health. Who chaired the meeting.
Prematurity And Cameroon’s Healthcare System
He added that Cameroon’s healthcare system is anchored on the Sustainable Development Goals and the National Development Strategy 30. And from these, strategies have been developed, especially on maternal, infant, newborn and adolescent care, with focus on the premature babies.
According to Dr Ngou Patrick, a pediatrician with Yaounde General Hospital, Ngoussou, the follow-up of premature or preterm babies is not only dependent on pediatrics, but also on other work that has to be done. “It is like a classroom where we give lessons to all those who manage the classroom – midwives, general practitioners, nurses,” Dr Ngou illustrated.
Everyone’s Concern
“We can't limit the care of premature babies only to the pediatrician and midwife. This is the message that had to be passed on. We must evaluate the gestation, refer the premature if need be, and ensure that the personnel who take care of premature babies master the technical gestures. So, the care of a premature babies in hospital is like intensive care,” he pointed out.
Kangaroo Mother Care Method
Nguidjol Jacqueline, a university student and mother of previously premature set of twins, recounted her traumatizing experience. “First, I was elated to have two boys at the same time. The first weighed 0.98 kilogrammes and the second, 0.99 kilogrammes. Efoulan District Hospital, Yaounde trained us in Kangaroo Mother Care, which we practised for sixth months until the twins regained weight. We managed the babies for three weeks in hospital using Kangaroo Mother Care, and the rest of the time was at home - all day, all night!” said Jacqueline.
Bonding With Babies
“Health personnel made life easier for the babies and saved them from many diseases by strengthening their immune system. The Kangaroo method enabled me to bond better with my babies from birth until today because we really understand each other. I am trying to adapt to every situation. It's not easy, but the children are in good health and I am happy to see them growing up healthily.
Cheaper Cost
“Without the Kangaroo Mother Care method, the financial cost of treating of the twins would have been more challenging because it involves doubling the expenses. Thank God, they are stable now. Today they are 1 year, 3 months old and they are in good health. It's a bit hard, but we are adapting very well,” Jacqueline admitted.
Causes Of Prematurity
There are numerous causes of preterm birth, some of which are identifiable and can be prevented to avoid the complications associated with prematurity. For this reason, the international community has dedicated an entire month to intensify interventions aimed at improving the survival of preterm infants.
Awareness
In response, the Government of Cameroon is mobilizing stakeholders to raise awareness. Various activities will be carried out nationwide, with a strong focus on mass and community communication to sensitize the population about the risks of prematurity and the importance of preventive actions. Particularly through optimal antenatal follow-up and appropriate management of preterm newborns.
Global Impact Of Prematurity
Each year, about 15 million babies are born prematurely worldwide - approximately one in ten births - leading to nearly one million deaths annually. Over 90 per cent of preterm infants born in low-income countries die within the first few days of life, compared to about 10 per cent in high-income countries. Furthermore, more than 60 per cent of preterm births occur in Africa and South Asia - regions most severely affected by this condition.
Cameroon Situation
In Cameroon, prematurity constitutes a major public health concern. Approximately 28 per cent or nearly three out of ten newborn deaths result from complications related to prematurity. Efforts to reduce infant mortality therefore require urgent actions in both prevention and management of preterm births. It is thus essential to inform and sensitize the general public nationwide about the challenges posed by prematurity in Cameroon.
Direct, Indirect Causes
Preterm births are caused by both direct and indirect factors. The direct factors are infections, anemia, malaria, and malnutrition; chronic maternal conditions such as diabetes and hypertension; and multiple pregnancies and congenital malformations. While the indirect prematurity causal factors are health-related. Such as unmonitored or poorly monitored pregnancies, low quality of care and services provided - particularly before, during, and after delivery - maternal age (under 18 or over 35 years), history of previous preterm birth, and similar factors.
Living conditions like distance from health facilities, physically demanding work or conditions (farming, household chores, carrying heavy loads, etc.) and early marriages are also responsible preterm births. Lastly, socio-economic conditions like low household income that limits the ability to pay for health services and care, such as antenatal consultations, and low coverage of universal health care or health insurance, account for this.
The Cost Of Prematurity
Meanwhile, t...
Cet article complet est réservé aux abonnés
Déjà abonné ? Identifiez-vous >
Accédez en illimité à Cameroon Tribune Digital à partir de 26250 FCFA
Je M'abonne1 minute suffit pour vous abonner à Cameroon Tribune Digital !
- Votre numéro spécial cameroon-tribune en version numérique
- Des encarts
- Des appels d'offres exclusives
- D'avant-première (accès 24h avant la publication)
- Des éditions consultables sur tous supports (smartphone, tablettes, PC)












Commentaires